Contents
Have you ever wondered why it is illegal to feed fish corn? It may seem like a harmless act, but there are actually valid reasons behind this restriction. In this article, we will explore the reasons why fish are not allowed to be fed corn, shedding light on the potential harm it can cause to aquatic ecosystems. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of fish feeding practices and uncover why corn is considered a big no-no!

1. Introduction
1.1 Overview of fish feeding practices
Feeding fish is an essential aspect of fishkeeping, whether in aquariums or in natural habitats. Proper nutrition is crucial for the overall health and well-being of fish, allowing them to thrive and maintain their natural behaviors. However, not all feeding practices are suitable or beneficial for fish populations. One such practice is the feeding of corn to fish, which has been deemed illegal in many regions due to its detrimental effects on the environment and fish health.
1.2 Introduction to the illegality of feeding fish corn
The illegality of feeding fish corn stems from the numerous environmental and ecological consequences associated with this practice. While corn may seem like a convenient and cost-effective option for feeding fish, it can have severe negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems, create nutritional imbalances, promote predatory behavior, lead to genetic pollution, and violate legal regulations. In order to protect fish populations and maintain the fragile balance of aquatic ecosystems, many governments and conservation efforts have implemented strict regulations and penalties against corn feeding.
2. Environmental Impacts
2.1 Disruption of aquatic ecosystems
Feeding fish corn can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems. When corn is introduced into water bodies, it can sink and accumulate on the bottom, leading to an alteration of the substrate composition. This disturbance can impact bottom-dwelling organisms, such as benthic invertebrates, by reducing their habitat availability and affecting their ability to find food. Additionally, the accumulation of corn residues can modify water flow patterns and hinder the natural movement of aquatic organisms, further disrupting the ecosystem’s functionality.
2.2 Disease transmission
Corn feeding also poses a risk of disease transmission among fish populations. When fish are fed corn, their immune systems may become compromised, making them more susceptible to infections and diseases. Additionally, the decomposition of uneaten corn can release toxins and harmful bacteria into the water, contributing to the spread of diseases among fish. This can have devastating effects on local fish populations and impair the overall health of the ecosystem.
2.3 Algae blooms
Feeding fish corn can contribute to the occurrence of harmful algae blooms. The excessive nutrients released from uneaten corn residues can promote the rapid growth of algae, leading to an overabundance of these organisms in the water. Algae blooms can have detrimental effects on fish and other aquatic organisms by depleting oxygen levels, blocking sunlight penetration, and creating toxic conditions. This can result in fish kills, upsetting the balance of the ecosystem and harming biodiversity.
2.4 Water quality degradation
The feeding of corn to fish can also result in water quality degradation. The decomposition of uneaten corn releases organic matter into the water, which can increase nutrient levels and alter the water’s chemical composition. Elevated levels of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, can lead to eutrophication, a process in which excessive nutrient enrichment promotes the growth of algae and other unwanted aquatic vegetation. This decrease in water quality can have cascading effects on the entire aquatic ecosystem, impacting not only fish but also other resident organisms.

3. Nutritional Imbalance
3.1 Incomplete diet
Feeding fish a diet comprised solely of corn can result in an incomplete and unbalanced nutritional profile. Corn lacks essential nutrients that fish require for optimal growth and development. While it may provide some calories, it falls short in providing fish with proper protein, vitamins, and minerals necessary for maintaining overall health. A diet lacking in essential nutrients can lead to various health issues and growth deficiencies in fish.
3.2 Lack of essential nutrients
Corn feeding fails to provide fish with vital nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for their growth, reproduction, and immune system function. Additionally, fish require essential amino acids, such as lysine and methionine, which are often insufficient in corn-based diets. The absence of these essential nutrients can lead to stunted growth, weakened immune systems, and increased vulnerability to diseases.
3.3 Growth retardation
Feeding fish corn exclusively can result in growth retardation and hinder their developmental potential. Fish reared on a corn-based diet may experience slower growth rates and exhibit smaller body sizes compared to fish fed a balanced and nutritious diet. This can have detrimental consequences for commercial fisheries, aquaculture operations, and overall fish populations, impacting the economic and ecological sustainability of these industries.
4. Predatory Behavior
4.1 Increased aggression
Feeding fish corn can lead to increased aggression and territorial behavior among fish populations. When fish rely solely on corn as their food source, competition for limited resources intensifies, leading to aggressive behaviors. Corn does not naturally occur as a prey item in fish habitats, and its introduction can disrupt the natural feeding dynamics, causing heightened aggression and stress levels among fish.
4.2 Adverse effects on natural prey populations
The feeding of corn to fish can have adverse effects on natural prey populations. Fish that are fed corn may become less efficient predators as their hunting instincts diminish due to the availability of an unnatural food source. This can lead to imbalances in predator-prey relationships, resulting in sudden declines in the populations of natural prey organisms. This disruption can have cascading effects throughout the food chain, potentially impacting other organisms dependent on these prey species.
4.3 Disturbance of the food chain
Corn feeding can disturb the natural food chain within aquatic environments. By introducing a non-native food source like corn, the delicate balance between primary producers, herbivores, and predators can be disrupted. This disruption can have far-reaching consequences, affecting the entire food web and leading to imbalances in ecosystem dynamics. The disturbance of the food chain can negatively impact both fish populations and the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.

5. Genetic Pollution and Hybridization
5.1 Risk of interbreeding
The feeding of corn to fish can increase the risk of interbreeding and hybridization between different fish species. When fish rely solely on corn as their food source, they may congregate and mix with other fish species that are also being fed corn. This increased interaction and intermingling of fish species can lead to hybridization, where genetic material from different species is combined, potentially diluting gene pools and compromising the genetic integrity of native fish populations.
5.2 Negative effects on genetic diversity
Feeding fish corn can have negative effects on genetic diversity within fish populations. Genetic diversity is crucial for a species’ resilience and adaptation to environmental changes. When fish populations interbreed due to corn feeding, genetic diversity may decrease, leading to reduced adaptive potential and increased vulnerability to environmental stressors. This decrease in genetic diversity can have long-term consequences for the survival and health of fish populations.
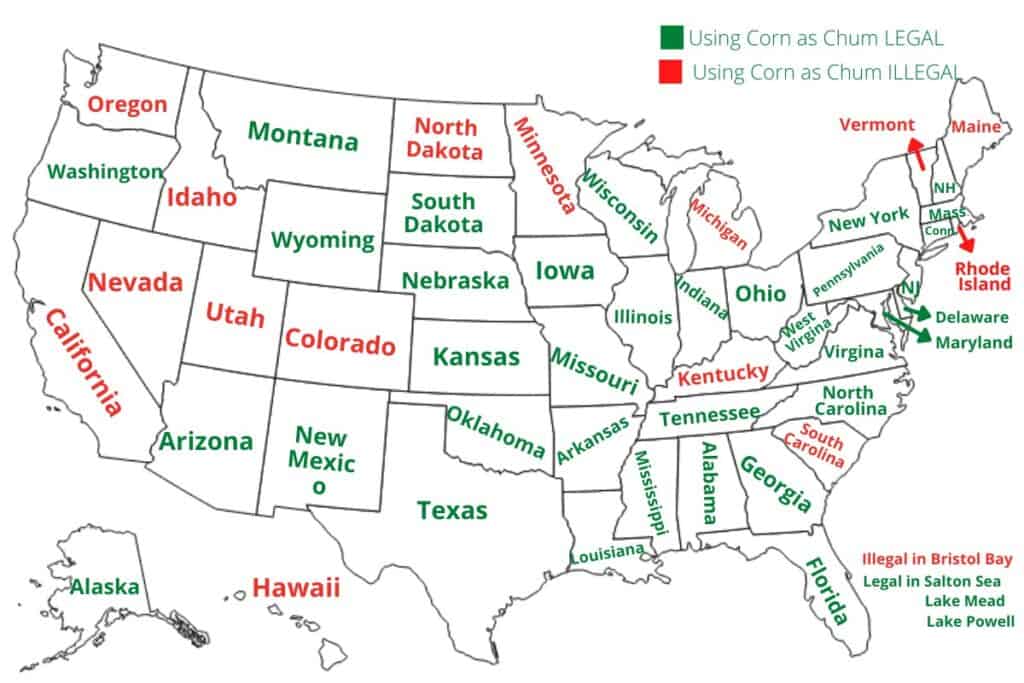
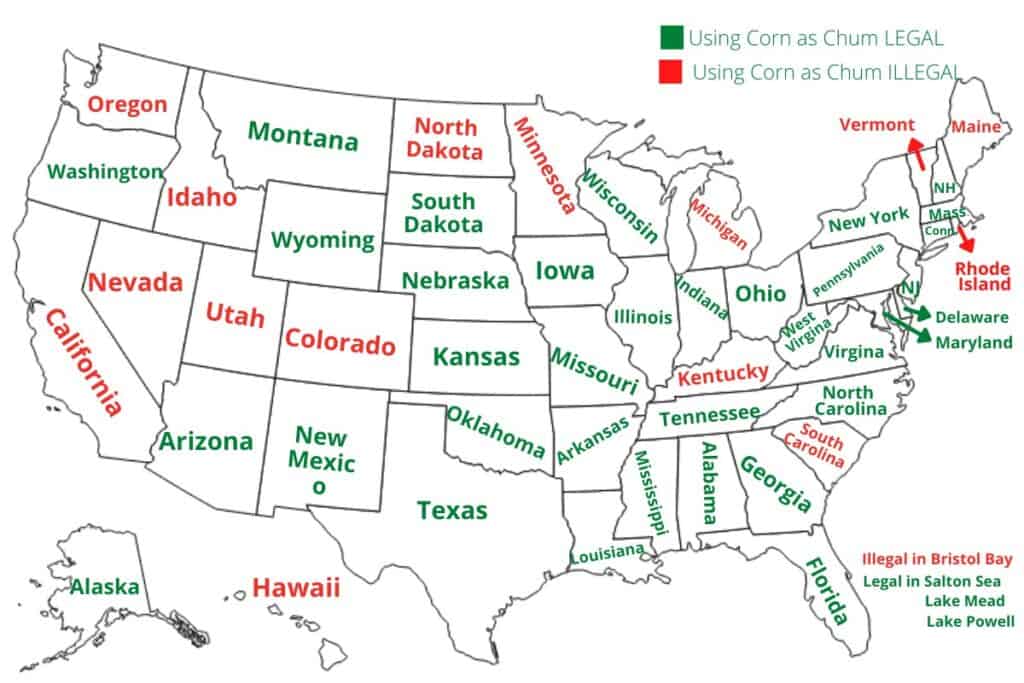
6. Legal Regulations
6.1 Government restrictions
Governments have implemented strict regulations to prohibit the feeding of fish with corn due to its significant negative impacts on the environment and fish populations. These restrictions aim to protect aquatic ecosystems, preserve biodiversity, and maintain the overall health and sustainability of fish habitats. It is essential for individuals and organizations involved in fishing and aquaculture operations to adhere to these regulations and seek sustainable and responsible alternatives to corn feeding.
6.2 Conservation efforts
Conservation efforts have been instrumental in spreading awareness about the detrimental effects of corn feeding and working towards its elimination. Conservation organizations actively engage in research, education, and advocacy to promote responsible fish feeding practices and emphasize the importance of preserving natural feeding behaviors and dietary requirements. By collaborating with stakeholders and governments, these efforts contribute to the overall protection and conservation of fish populations and their habitats.
6.3 Penalties and fines
Violations of the laws that prohibit feeding fish corn can result in penalties and fines imposed by authorities. These penalties serve as a deterrent to individuals and organizations who may consider engaging in this illegal practice. By enforcing strict consequences, governments discourage the feeding of corn to fish and emphasize the seriousness of the environmental and ecological impacts associated with this behavior.

7. Alternatives to Corn Feeding
7.1 Natural fish feed
To ensure the nutritional needs of fish are met without resorting to corn feeding, various natural fish feed options are available. These alternatives are formulated to provide a balanced and complete diet for fish, containing essential nutrients, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Natural fish feed can be sourced from a variety of ingredients, such as fish meal, shrimp meal, algae, and plant-based proteins. These feeds aim to replicate a fish’s natural diet while promoting optimal growth and minimizing environmental impacts.
7.2 Sustainability practices
Sustainability practices, such as implementing proper feeding protocols and carefully monitoring fish populations, can help mitigate the need for corn feeding. By conducting regular assessments of fish health and growth, adjusting feeding regimes based on nutritional requirements, and ensuring proper waste management, fish farmers and hobbyists can maintain healthy fish populations while minimizing environmental impacts. Additionally, supporting sustainable fisheries and aquaculture operations encourages responsible fish feeding practices and contributes to the overall health of aquatic ecosystems.
7.3 Aquatic ecosystem preservation
Preserving the natural integrity of aquatic ecosystems is essential for the well-being of fish populations. By advocating for habitat conservation, protecting wetlands, and promoting responsible land and water management practices, individuals and organizations can contribute to the preservation of aquatic ecosystems. Healthy ecosystems provide diverse and natural food sources for fish, reducing the reliance on artificial and unnatural feeding practices like corn feeding.
8. Case Studies
8.1 Impact of corn feeding in specific regions
In specific regions where corn feeding has been prevalent, studies have documented the severe impacts on aquatic ecosystems and fish populations. For example, in certain lakes and rivers where illegal corn feeding was widespread, significant declines in water quality, disruptions in the natural food chain, and negative influences on native fish species were observed. These case studies highlight the urgency for intervention and emphasize the need for strict regulations to combat the detrimental effects of corn feeding.
8.2 Success stories in banning corn feeding
On a positive note, there have been success stories in regions where corn feeding has been effectively banned. Through rigorous enforcement of regulations, educational campaigns, and promoting sustainable fish feeding practices, these success stories demonstrate the potential for change and environmental restoration. With the removal of corn feeding, fish populations have rebounded, ecosystem functions have been restored, and the overall health and diversity of aquatic habitats have improved.
9. Awareness and Education
9.1 Promoting responsible fish feeding practices
Raising awareness about responsible fish feeding practices is crucial in reducing the prevalence of corn feeding. By disseminating information about the environmental impacts, legal regulations, and alternative feeding options, individuals can make informed decisions and actively contribute to the well-being of fish populations. Promoting responsible fish feeding practices includes educating fishkeepers, anglers, and aquaculture industries about the importance of providing a balanced diet, avoiding harmful feeding practices, and supporting sustainable alternatives.
9.2 Engaging fishermen and aquaculture industries
Engaging fishermen and the aquaculture industry is essential for effecting change and moving towards sustainable fish feeding practices. By fostering dialogue, providing resources and support, and highlighting the benefits of responsible feeding, fishermen and industry professionals can be encouraged to adopt alternative feeding methods that prioritize the health of fish populations and the preservation of aquatic ecosystems. Collaboration and knowledge sharing are key in driving the necessary shifts in feeding practices.
9.3 Public campaigns and advocacy
Public campaigns and advocacy play a vital role in raising awareness about the illegality and harmfulness of corn feeding. By implementing targeted campaigns through various media platforms, such as social media, television, and print, individuals and organizations can reach a broader audience and educate the public about the impact of their feeding choices on fish and the environment. Additionally, advocacy efforts can include lobbying for stricter regulations, supporting sustainability initiatives, and empowering communities to take action and protect their local fish habitats.
10. Conclusion
The illegality of feeding fish corn is rooted in the understanding of its detrimental effects on the environment and fish populations. From disrupting aquatic ecosystems to causing nutritional imbalances, promoting predatory behavior, and leading to genetic pollution, the negative consequences of corn feeding are extensive. Legal regulations, conservation efforts, and the promotion of sustainable alternatives provide viable solutions to mitigate the harmful impacts of corn feeding. By raising awareness, engaging stakeholders, and advocating for responsible fish feeding practices, we can ensure the long-term health and sustainability of fish populations and their habitats.