Contents
- What is a small appliance according to the EPA?
- Definition of a Small Appliance
- EPA Regulations for Small Appliances
- Examples of Small Appliances
- Importance of Proper Disposal
- Benefits of Small Appliance Recycling
- Stakeholders in Small Appliance Recycling
- Challenges and Barriers to Small Appliance Recycling
- Impacts of Small Appliance Waste
- E-waste Management and Small Appliances
- Future Sustainability Initiatives
In this informative article, you will discover the official definition of a small appliance according to the EPA. Gain a clear understanding of what falls under this category as the EPA provides their distinct criteria. Whether you’re curious about the devices in your home or interested in energy efficiency, this article will shed light on the classification of small appliances as defined by the EPA. Let’s delve into it!
What is a small appliance according to the EPA?

Definition of a Small Appliance
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), a small appliance refers to any electronic or electric device that is designed for household use, small-scale commercial purposes, or personal use that is typically portable. These appliances are generally characterized by their compact size, lightweight, and ability to perform specific tasks. The EPA defines small appliances as those that are powered by batteries, plug into an electrical outlet, or use alternative power sources such as solar energy.
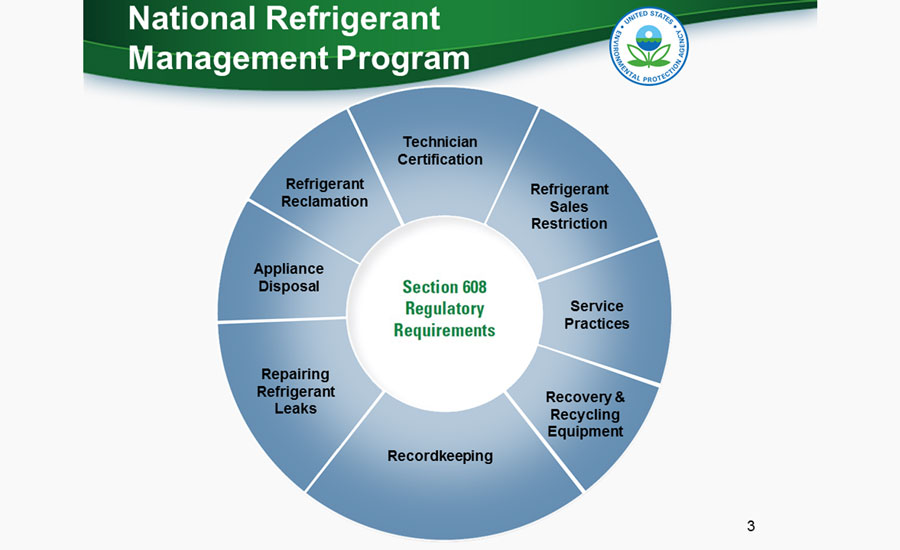
EPA Regulations for Small Appliances
The EPA has put in place specific regulations and guidelines to govern the management and disposal of small appliances. These regulations aim to ensure the proper handling, recycling, and safe disposal of these devices to minimize their impact on the environment. Small appliances often contain hazardous materials and components, such as lead, mercury, and other toxic substances, which can pose significant risks if not handled properly. The EPA encourages individuals and businesses to adhere to these regulations to protect the environment and human health.

Examples of Small Appliances
Examples of small appliances include but are not limited to:
- Toaster ovens
- Blenders
- Coffee makers
- Hair dryers
- Electric toothbrushes
- Electric shavers
- Irons
- Vacuum cleaners
- Handheld mixers
- Electric fans
These appliances are commonly found in households, offices, and various industries, contributing to the daily convenience and efficiency of our lives.
Importance of Proper Disposal
Proper disposal of small appliances is essential for several reasons. First and foremost, it helps prevent potential harm to the environment and human health. Many small appliances contain toxic substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can contaminate soil, water sources, and the air if not handled and disposed of correctly.
Additionally, proper disposal ensures that valuable materials within these appliances can be recovered and recycled. Recycling small appliances helps conserve natural resources, reduce energy consumption, and minimize the need for extracting and manufacturing new materials. By disposing of small appliances appropriately, we can contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
Benefits of Small Appliance Recycling
Recycling small appliances offers numerous benefits to both the environment and society. Firstly, it reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, helping to alleviate the strain on these already overburdened sites. By diverting small appliances from landfills, we can make room for other non-recyclable waste and extend the lifespan of these disposal facilities.
Secondly, small appliance recycling plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. When these devices are incinerated or decomposed in landfills, they can release harmful gases into the atmosphere. By recycling small appliances, we can recover valuable materials and reduce the need for resource-intensive extraction and manufacturing processes, thereby mitigating the associated carbon emissions.
Furthermore, recycling small appliances creates job opportunities in the recycling industry, contributing to local economies and promoting sustainable development. This industry requires skilled workers to disassemble, sort, and process the various components of small appliances. By supporting small appliance recycling initiatives, we can foster economic growth while protecting the environment.
Stakeholders in Small Appliance Recycling
The successful management and recycling of small appliances involve various stakeholders working together to achieve a common goal. These stakeholders include:
-
Consumers: As the end-users of small appliances, consumers play a vital role in the recycling process. They can contribute by responsibly disposing of their old appliances, participating in recycling programs, and choosing energy-efficient and environmentally friendly products.
-
Manufacturers: Small appliance manufacturers have a responsibility to design products that are both functional and environmentally conscious. They can promote recycling by establishing take-back programs, using recyclable materials, and reducing the use of hazardous substances in their products.
-
Retailers: Retailers play a crucial role in promoting small appliance recycling by providing collection points for old appliances and educating their customers about proper disposal methods. They can also incentivize recycling by offering discounts or trade-in programs for new purchases.
-
Recycling Facilities: These facilities are responsible for the proper processing and recycling of small appliances. They must adhere to strict environmental regulations and employ advanced technologies to safely extract valuable materials from these devices.
-
Government and Regulatory Bodies: Governments play a significant role in establishing and enforcing regulations to ensure the proper management of small appliances. Regulatory bodies, such as the EPA, provide guidelines and oversight to promote responsible disposal and recycling practices.

Challenges and Barriers to Small Appliance Recycling
While small appliance recycling offers numerous benefits, there are also several challenges and barriers that need to be addressed. These include:
-
Lack of Awareness: Many people are unaware of the importance of recycling small appliances or the potential environmental and economic benefits it offers. Increasing public awareness through educational campaigns and outreach programs is crucial to overcoming this barrier.
-
Limited Collection Infrastructure: In some areas, there may be a lack of proper collection facilities or drop-off points for small appliances. To encourage recycling, it is essential to develop accessible and convenient collection infrastructure where consumers can easily dispose of their old devices.
-
Lack of Incentives: Without proper incentives, individuals may be less motivated to participate in small appliance recycling programs. Offering financial incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, can encourage consumer involvement and make recycling a more attractive option.
-
Complex Disassembly Process: Small appliances often contain a wide range of materials and components, making their disassembly and recycling complex. Developing innovative technologies and processes to efficiently extract valuable materials can help overcome this challenge.
Impacts of Small Appliance Waste
The improper management and disposal of small appliances can have significant impacts on the environment and human health. When these devices end up in landfills or are incinerated, hazardous substances can leach into the soil and contaminate groundwater, posing risks to ecosystems and wildlife.
Furthermore, the mining and extraction of raw materials to manufacture new appliances contribute to deforestation, habitat destruction, and increased carbon emissions. By recycling small appliances, we can reduce the demand for new materials and lessen the environmental impact associated with their production.

E-waste Management and Small Appliances
Small appliances are a subset of electronic waste (e-waste), which refers to any discarded electronic or electric device. Managing e-waste, including small appliances, is essential due to the rapid growth in electronic consumption worldwide. E-waste contains valuable materials and hazardous substances, requiring specialized recycling processes to extract and recover valuable resources while minimizing environmental risks.
To effectively manage small appliance e-waste, it is crucial to establish comprehensive recycling programs, strengthen regulations, and promote innovation in e-waste management technologies. By adopting responsible e-waste management practices, we can mitigate the environmental and health risks associated with these discarded devices.
Future Sustainability Initiatives
Looking ahead, it is essential to continue promoting sustainability initiatives surrounding small appliance recycling. This includes raising public awareness, investing in research and technological advancements, and collaborating across sectors to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling processes.
Moreover, governments should consider implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products. These policies encourage manufacturers to design products that are easier to recycle, provide funding for collection and recycling programs, and promote circular economy principles.
By embracing these future sustainability initiatives, we can work towards a more sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to small appliance management and recycling. Together, we can minimize waste generation, conserve resources, and create a greener future for generations to come.