Contents
- Understanding the Nutritional Needs of Fish
- Types of Fish Feed
- Feeding Frequency and Quantity
- Choosing the Right Feeding Method
- Feeding Strategies for Different Fish Species
- Feeding Tips and Techniques
- Feeding Challenges and Solutions
- Feeding Fish in Different Habitats
- Special Considerations and Precautions
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
In “The Ultimate Guide to Fish Feeding,” you will discover a wealth of valuable information to ensure your aquatic pets are well-nourished and thrive in their habitat. From understanding the nutritional needs of different fish species to mastering the art of feeding techniques, this guide will equip you with all the tips and tricks necessary to become a knowledgeable and responsible fish keeper. So, whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or just starting out, get ready to embark on an exciting journey to enhance your fish’s health and happiness with the ultimate feeding guide.
Understanding the Nutritional Needs of Fish
Importance of a Balanced Diet
When it comes to keeping fish healthy and thriving, providing them with a balanced diet is of utmost importance. Just like humans, fish require a variety of nutrients to support their growth, reproduction, and overall well-being. A balanced diet for fish ensures that they receive all the essential nutrients in the right proportions. This helps to prevent nutritional deficiencies and related health issues.
Protein Requirements
Protein is a crucial component of a fish’s diet as it is responsible for building and repairing tissues, promoting growth, and supporting immune function. Different species of fish have varying protein requirements, and it is essential to meet these needs to ensure their optimal health. Protein can be obtained from various sources such as fish meal, shrimp meal, soybean meal, and blood meal. It is important to choose a feed that provides a sufficient amount of high-quality protein for your specific fish species.
Carbohydrates and Fats
While protein is the primary source of energy for fish, carbohydrates and fats also play important roles in their nutrition. Carbohydrates provide a readily available source of energy, while fats provide a concentrated energy source and help with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Including carbohydrates and fats in a fish’s diet in appropriate amounts is crucial to ensure their energy needs are met.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are micronutrients that play essential roles in fish health. They are involved in various physiological processes, including metabolism, immune function, and reproduction. Fish require a range of vitamins such as vitamin A, B, C, D, and E, as well as minerals like calcium, phosphorus, iron, and zinc. Providing a well-balanced fish feed that contains a variety of vitamins and minerals is vital to meet their nutritional requirements.
Types of Fish Feed
Commercial Fish Feed
Commercial fish feeds are widely available and are formulated to provide a balanced diet for different species of fish. They come in various forms, including pellets, flakes, and granules. Commercial fish feeds are convenient to use and often contain a mix of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. It is essential to choose a high-quality commercial feed that is specifically designed for the species of fish you are keeping.
Live and Frozen Foods
Live and frozen foods are beneficial for fish as they provide a more natural and varied diet. Live foods such as brine shrimp, daphnia, and bloodworms are rich in nutrients and can stimulate a fish’s natural foraging behavior. Frozen foods such as krill, mysis shrimp, and fish fillets are convenient alternatives that can be stored for a longer time. These types of foods can be used as occasional treats or as a supplement to a fish’s regular diet.
Homemade Fish Feed Recipes
Some fish owners prefer to make their own fish feed to have better control over the ingredients and nutritional content. Homemade fish feed recipes often include a combination of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Common ingredients used in homemade fish feed include fish meal, shrimp meal, vegetable matter, and gelatin. It is important to ensure that the homemade feed is properly balanced and meets the specific nutritional needs of the fish species.

Feeding Frequency and Quantity
Determining the Ideal Feeding Frequency
The feeding frequency for fish varies depending on their species, age, and size. As a general guideline, most fish should be fed once or twice a day. However, some species may require more frequent feedings, while others may need less. Observe your fish’s behavior and adjust the feeding frequency accordingly. It is important not to overfeed, as this can lead to water pollution and health issues.
Calculating the Right Amount of Feed
Determining the correct quantity of feed to give your fish can be challenging. Overfeeding can result in uneaten food accumulating in the tank, which can dirty the water and negatively impact water quality. Underfeeding, on the other hand, can lead to malnutrition and stunted growth. A general rule of thumb is to feed your fish an amount they can consume in a few minutes. Monitor their eating habits and adjust the quantity accordingly.
Feeding Guidelines for Different Fish Species
Each fish species has its own specific feeding requirements, and it is important to research and understand the needs of your particular fish. Some species are grazers and require continuous access to small amounts of food, while others are predatory and need larger meals less frequently. Pay attention to the feeding recommendations provided for your specific fish species and adjust their diet accordingly.
Choosing the Right Feeding Method
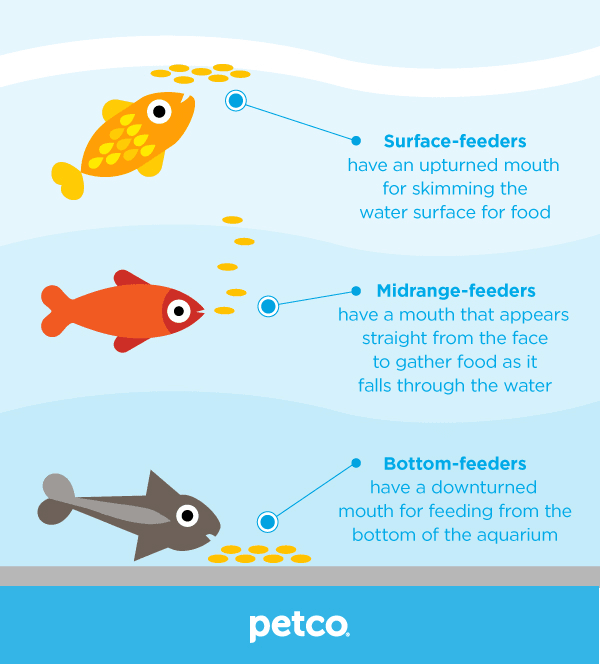
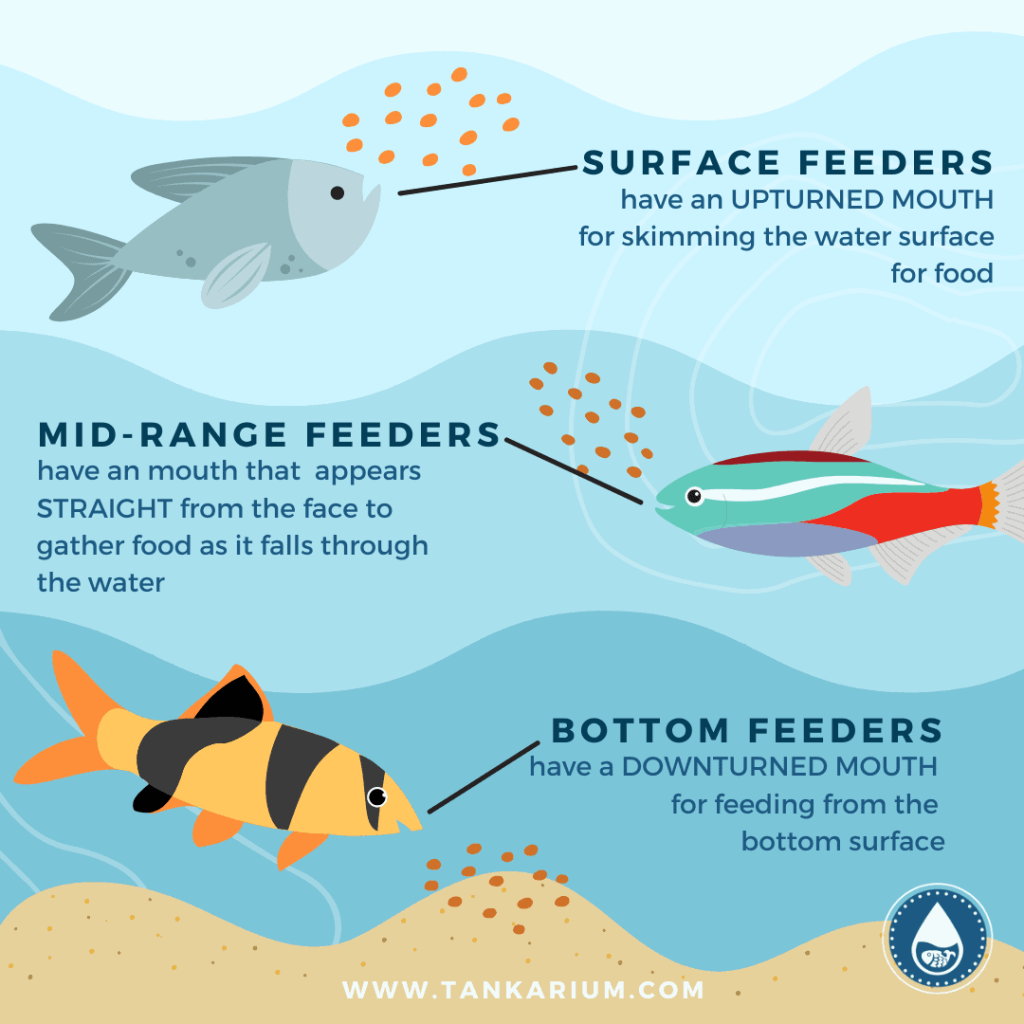
Floating Pellets
Floating pellets are a popular choice for feeding fish, as they are convenient and allow for easy monitoring of feeding behavior. These pellets float on the water’s surface, making them easily accessible to fish that swim near the top of the tank. They are suitable for various fish species, including surface-dwelling and mid-water swimmers.
Sinking Pellets
Sinking pellets are designed to sink to the bottom of the tank, making them suitable for bottom-dwelling and scavenging fish. These pellets ensure that fish that prefer to feed near the substrate receive their share of food. However, it is important to observe feeding behavior and ensure that all fish have access to the sinking pellets.
Freeze-Dried and Freeze-Fried Foods
Freeze-dried and freeze-fried foods are convenient options that provide a diverse diet for fish. They are made by removing water from the food while maintaining most of its nutritional value. Freeze-dried and freeze-fried foods come in various forms such as bloodworms, daphnia, and brine shrimp. These foods can be rehydrated before feeding or used as occasional treats.
Gel-Based Foods
Gel-based foods are becoming increasingly popular as they offer a customizable and nutritious feeding option. These foods are made by mixing a variety of ingredients such as proteins, vegetables, and vitamins with a gelatin base. The mixture is then shaped into cubes or sheets that can be easily portioned and fed to fish. Gel-based foods provide a balanced diet and can be tailored to the specific needs of individual fish species.
Liquid and Paste Foods
Liquid and paste foods are another option for feeding fish, particularly species that have small mouths or require specialized diets. These foods come in liquid or paste form and can be directly administered to the fish or smeared onto surfaces for them to graze on. Liquid and paste foods are often fortified with vitamins and minerals, providing a complete and easily digestible source of nutrition.
Grazing and Plant-Based Diets
Some fish, particularly herbivorous species, require a grazing or plant-based diet. They thrive on an assortment of fresh or blanched vegetables, algae wafers, and plant-based fish foods. Providing these fish with a variety of plant-based options ensures they receive the necessary nutrients to support their unique dietary needs.

Feeding Strategies for Different Fish Species
Carnivorous Fish
Carnivorous fish, such as cichlids and predatory species, require a high-protein diet consisting of meat-based foods. These fish should be fed a variety of protein-rich foods such as fish fillets, shrimp, and insects. It is essential to closely monitor their feeding to prevent overfeeding and to ensure that they receive a balanced diet.
Herbivorous Fish
Herbivorous fish, like many species of cichlids and plecos, have specialized dietary requirements. They primarily feed on plant matter and require a diet rich in fiber and nutrients. Providing them with a variety of vegetables, algae wafers, and plant-based fish foods is essential to support their health and digestion.
Omnivorous Fish
Omnivorous fish, such as guppies and tetras, have flexible dietary needs and can thrive on a combination of plant matter and protein-based foods. It is important to offer them a balanced diet that includes both plant-based and protein-rich options. This can be achieved by regularly feeding them a combination of commercial fish feed, live or frozen foods, and vegetables.
Bottom-Dwelling Fish
Bottom-dwelling fish, such as catfish and loaches, have unique feeding habits. They scavenge for food on the substrate and prefer sinking foods that reach the bottom of the tank. Sinking pellets, freeze-dried foods, and gel-based foods are ideal options for these fish. It is important to ensure that bottom-dwelling fish get their fair share of food and are not outcompeted by faster-swimming species.
Feeding Tips and Techniques
Observe Fish Behavior
Observing your fish’s behavior during feeding can provide valuable insights into their nutritional needs. Pay attention to their appetite, feeding speed, and interaction with the food. If a fish is consistently not eating, it may be an indication of an underlying health issue or feeding preference. Adjust their diet accordingly or seek professional advice if necessary.
Avoid Overfeeding
One of the most common mistakes in fish feeding is overfeeding. Overfeeding can lead to excessive waste, poor water quality, and health issues for your fish. Only feed your fish an amount that they can consume within a few minutes, and avoid leaving uneaten food in the tank. It is better to slightly underfeed than to overfeed, as fish can survive for longer periods without food than with excess food.
Avoid Underfeeding
While overfeeding is a common mistake, underfeeding can also have detrimental effects on fish health. Insufficient nutrition can lead to malnutrition, stunted growth, and weakened immune systems. Ensure that you are providing your fish with a balanced diet that meets their specific nutritional needs. If in doubt, consult a veterinarian or aquatic expert for guidance.
Adjusting Feeding Habits
Fish’s feeding habits can change over time, depending on factors such as growth, age, reproductive status, and health. It is important to monitor their behavior and adjust their feeding habits accordingly. For example, growing fish may require more frequent feedings, while fish that are spawning or recovering from illness may need specialized diets. Stay attentive to their needs and adapt their feeding routine as necessary.
Feeding During Different Stages of Life
Fish have different nutritional needs at different stages of life. Fry and juveniles require more frequent feeding and smaller food particles to support their rapid growth. Adult fish may have different dietary needs depending on their reproductive status and health. It is crucial to research and understand the specific dietary requirements of your fish at each life stage to ensure their optimal growth and well-being.

Feeding Challenges and Solutions
Dealing with Picky Eaters
Some fish can be picky eaters and may refuse certain types of food. This can be challenging and may require some trial and error to find a suitable diet that they will accept. Experiment with different types of commercial fish feed, live or frozen foods, and homemade recipes to entice the fish to eat. It may also help to incorporate some variety into their diet to keep their interest and appetite stimulated.
Feeding Aggressive Fish
Feeding aggressive fish can be tricky, as they may exhibit territorial behavior during feeding. It is important to ensure that all fish have fair access to food and are not bullied or stressed by more aggressive individuals. One strategy is to use multiple feeding points in the tank to distribute the food and allow all fish to feed without competition. Another approach is to feed aggressive fish separately or at different times to prevent conflicts during feeding.
Solving Issues with Floating Pellets
Floating pellets may not be suitable for all fish species, as some may have difficulty locating and consuming the food at the water’s surface. To address this issue, you can pre-soak the pellets before feeding to make them sink faster. Alternatively, you can crush the pellets into smaller particles that will sink more easily. Observing your fish’s behavior during feeding will help you determine the best method to ensure they are getting their fair share of food.
Ensuring Proper Nutrition for Fry and Juveniles
Fry and juveniles have specific nutritional needs to support their rapid growth. They require small and nutrient-dense food particles that are easily digestible. Specialized fry food, baby brine shrimp, and infusoria are popular options for feeding fry and juveniles. It is important to provide multiple small feedings throughout the day to accommodate their high metabolic rates and ensure they receive sufficient nutrition for healthy development.
Feeding Fish in Different Habitats
Freshwater Aquarium Fish
Feeding freshwater aquarium fish requires understanding their specific dietary needs. Research the dietary requirements of your freshwater fish species and provide a balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs. Depending on the species, this may include a combination of commercial fish feed, live or frozen foods, and plant matter. Remember to feed your freshwater fish in moderation and maintain good water quality to support their overall health.
Saltwater Aquarium Fish
Saltwater aquarium fish have specific dietary needs to support their unique physiological requirements. Marine fish often require a protein-rich diet that includes various types of fish and shellfish-based foods. It is important to research the specific dietary requirements of your saltwater fish species and provide a balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs. Monitor water quality closely, as saltwater aquariums are more sensitive to fluctuations caused by overfeeding.
Pond Fish
Feeding fish in a pond environment can be quite different from feeding aquarium fish. Pond fish often rely on natural food sources such as insects, algae, and other aquatic organisms. Supplementing their diet with commercial fish feed can help ensure they are receiving a balanced diet. It is important to closely monitor their feeding behavior and adjust the quantity of food provided to prevent overfeeding and water pollution in the pond.
Aquaponics Systems
In aquaponics systems, fish play a vital role in the overall ecosystem. They provide the nutrients needed for the growth of plants, while the plants help filter the water for the fish. Feeding fish in an aquaponics system involves providing them with a balanced diet that supports their health and growth while also considering the nutritional needs of the plants. A combination of commercial fish feed, live or frozen foods, and plant matter can be used in these systems to meet the requirements of both the fish and plants.
Special Considerations and Precautions
Avoiding Overcrowding
Overcrowding can lead to competition for resources, including food. It is important to maintain appropriate stocking levels in fish tanks and ponds to ensure that each fish has access to sufficient food. Overcrowding can result in underfed fish, increased stress levels, and potential health issues. Research the appropriate stocking levels for your specific fish species and provide ample space to avoid overcrowding.
Preventing Water Pollution
Feeding practices can significantly impact water quality in fish tanks and ponds. Overfeeding or providing excessive amounts of food can lead to uneaten food sinking to the bottom and decomposing, resulting in poor water quality and harmful ammonia spikes. Regularly monitor water parameters such as ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and pH levels to ensure that the feeding practices do not negatively impact the overall water quality.
Handling Live and Frozen Foods Safely
Live and frozen foods, such as brine shrimp and bloodworms, should be handled and stored with care to maintain their nutritional value and prevent bacterial contamination. Follow the instructions provided with the food packaging and ensure that it is stored at the recommended temperature. Rinse live foods thoroughly before feeding to remove any impurities. Additionally, avoid overstocking on live foods, as they may introduce unwanted organisms or cause water quality issues if not consumed promptly.
Dealing with Fish Diseases Related to Feeding
Certain diseases in fish can be linked to their dietary habits. Nutritional imbalances, poor diet quality, or overfeeding can weaken a fish’s immune system and make them more susceptible to infections and diseases. Ensuring a balanced diet, providing high-quality feed, and maintaining proper feeding practices can help prevent these issues. If your fish show signs of illness, consult a veterinarian or aquatic expert for guidance on diagnostic and treatment options.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Feeding Inconsistency
Inconsistency in feeding routines can negatively impact fish health and digestion. Establish a regular feeding schedule for your fish and stick to it as closely as possible. Sudden changes or skipping feedings can lead to poor appetite, improper growth, and stress for your fish. Consistency in feeding practices helps maintain a healthy and stress-free environment for your fish.
Using Incorrect Feed
Using the wrong type of feed for your fish species can result in nutritional deficiencies or digestive issues. Research the dietary requirements of your fish species and use a feed that is formulated to meet those needs. Avoid using feed intended for other species or generic feeds that may not provide the necessary nutrients. Investing in high-quality feed specifically designed for your fish species will help ensure their overall health and well-being.
Feeding at Inappropriate Intervals
Feeding fish at incorrect intervals can disrupt their natural feeding behavior and lead to excessive or inadequate food intake. Research the feeding habits of your fish species and provide feed at appropriate intervals throughout the day. Avoid overfeeding by offering small, frequent meals instead of one large feeding. It is important to find the right balance to ensure that your fish receive enough nutrition without compromising their digestive health.
Ignoring Individual Fish Needs
Each fish in your tank or pond may have individual dietary needs and preferences. Pay attention to the behavior and feeding habits of each fish and adjust their diet accordingly. Some fish may be more active and require more food, while others may be picky eaters or have specific dietary requirements. Taking the time to understand and cater to each fish’s needs will help ensure their overall health and happiness.