Contents
- Definition of Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
- Characteristics
- Types
- Importance in Ecosystem
- Physical Features of Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
- Habitat and Distribution
- Feeding Behavior of Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
- Role in Marine Ecosystem
- Common Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish Species
- Behavior and Reproduction
- Challenges Faced by Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
- Conservation Efforts and Management
- Conclusion
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating creatures that inhabit the depths of the world’s oceans? In this article, we will explore the intriguing world of saltwater bottom feeder fish. These unique creatures play a vital role in the marine ecosystem, as they scavenge the ocean floor for food and act as nature’s cleaners. From their unusual appearances to their remarkable feeding habits, we will uncover the hidden secrets of these unsung heroes of the sea. So, prepare to dive into the mesmerizing world of saltwater bottom feeder fish and discover the wonders that lie beneath the surface.

Definition of Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
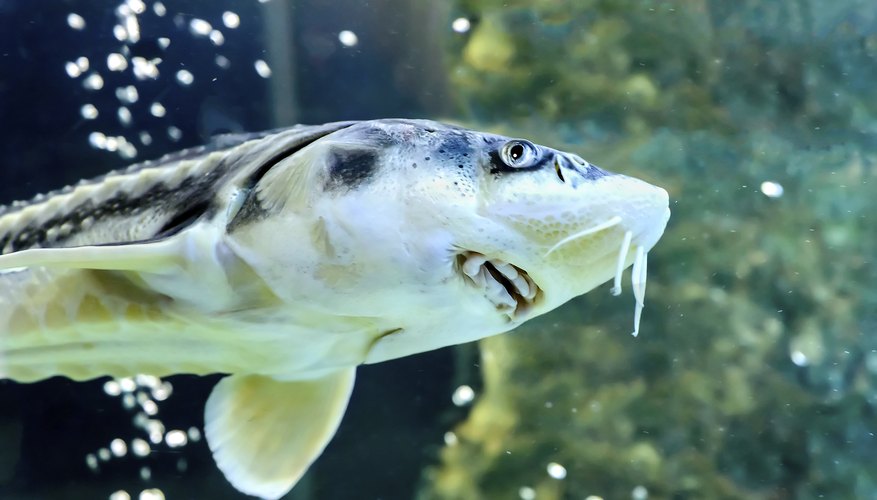
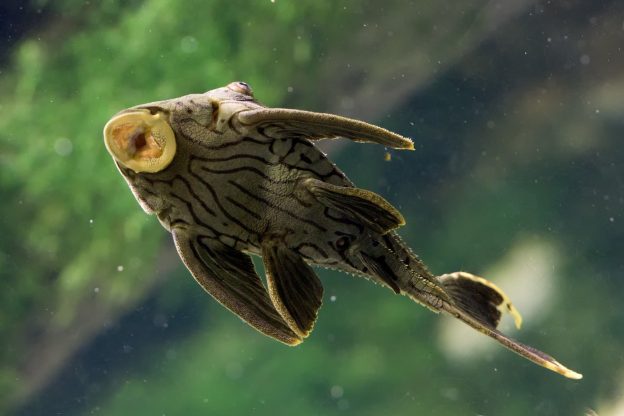
Saltwater bottom feeder fish refer to a group of marine fish species that thrive and primarily feed on the ocean bottom or substrate. These fish have adapted to their unique habitat and play an important role in the marine ecosystem. They are characterized by their feeding behavior, physical features, and their vital contributions to the overall health and balance of the ocean environment.
Characteristics
Saltwater bottom feeder fish exhibit several distinguishing characteristics that make them well-suited for their ecological niche. Typically, these fish have flattened bodies and are relatively small in size compared to other marine species. This body shape enables them to navigate easily along the ocean floor and take advantage of the abundant food sources found in this habitat.
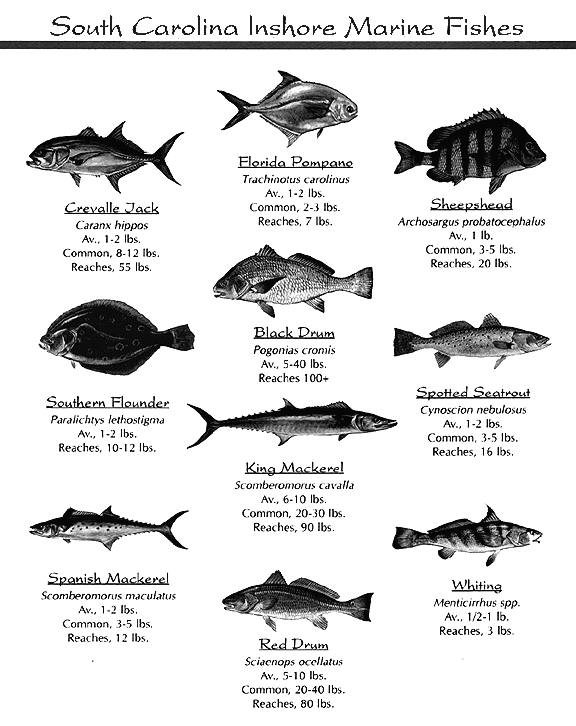
Types
There are various types of saltwater bottom feeder fish, each with its own unique set of characteristics and adaptations. Some commonly known species include catfish, triggerfish, flounder, gobies, and parrotfish. While each species has its own specific traits, they all share the common characteristic of being bottom feeders, utilizing similar feeding strategies and habitat preferences.
Importance in Ecosystem
Saltwater bottom feeder fish play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of marine ecosystems. As bottom-dwelling organisms, they actively contribute to the recycling of nutrients and the cleaning of the ocean floor. Additionally, they serve as a vital food source for larger predators, thus supporting the intricate food web of the underwater world. Furthermore, these fish species can act as indicators of environmental health, reflecting any changes or disturbances occurring within their habitat.

Physical Features of Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
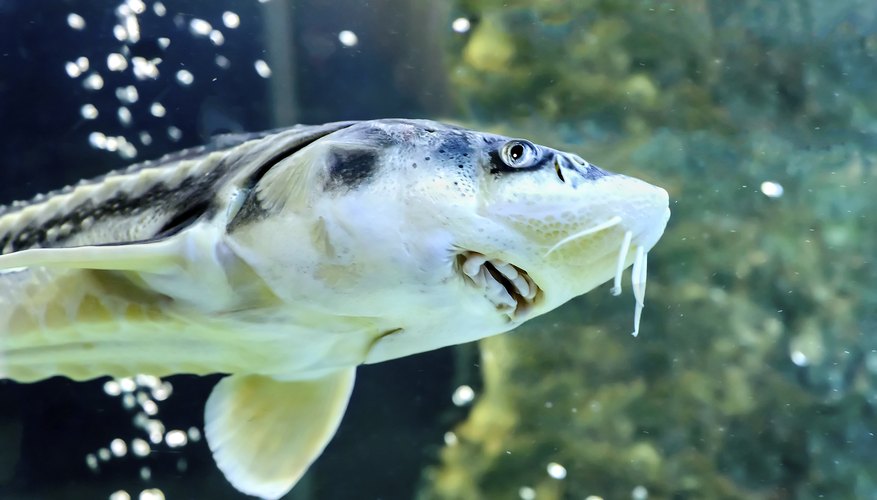
Body Shape and Size
Saltwater bottom feeder fish often have a flattened body shape, which allows them to navigate through the uneven terrain of the ocean floor with ease. This streamlined form assists in conserving energy and enables them to efficiently forage for food. In terms of size, these fish generally range from a few inches up to a foot in length, depending on the specific species.
Mouth and Jaw Structure
The mouths and jaw structures of saltwater bottom feeder fish are specifically adapted to facilitate their feeding habits. They commonly possess downward-facing mouths, equipped with strong jaws and specialized teeth. This arrangement enables them to scavenge and graze along the substrate, consuming various organisms and detritus found on the ocean floor.
Fins and Tails
The fins and tails of these fish are designed to provide stability and maneuverability. Their fins are often positioned closer to the front of the body, allowing for precise control of movement while navigating the bottom. The shape and size of their tails may vary among species, but all aid in propelling the fish along the substrate.
Coloration and Camouflage
Many saltwater bottom feeder fish display intricate coloration and patterns that allow them to blend seamlessly with their surroundings. They may exhibit earth-tone shades, mottled patterns, or even possess the ability to change colors to mimic the environment. These adaptations provide them with effective camouflage, helping them avoid predators and ambush their prey.
Habitat and Distribution
Coastal Areas and Reefs
Saltwater bottom feeder fish are commonly found in coastal areas and coral reefs. The coastal zone serves as a rich feeding ground for these species, where they can scavenge for food particles and small organisms in the sandy or rocky bottom. Coral reefs, with their diverse array of habitats and crevices, provide an abundance of food sources for these fish.
Deep Sea
Some saltwater bottom feeder fish inhabit the depths of the deep sea, where they reside in complete darkness. These elusive species have adapted to extreme pressure and temperature conditions, as well as scarce food resources. Their bottom-dwelling behavior in these deep-sea environments contributes to the overall functioning of the ecosystem beyond the reach of sunlight.
Tropical and Temperate Regions
Saltwater bottom feeder fish can be found in both tropical and temperate regions around the world. In tropical waters, where biodiversity is high, these fish exploit the vast array of food sources present along the ocean floor. In contrast, in temperate regions, they may rely on different prey items and adapt to seasonal variations in food availability.
Migration Patterns
Migration is a common behavior observed in some saltwater bottom feeder fish species. These migrations may occur over considerable distances, as the fish seek optimal feeding grounds or breeding sites. The timing and extent of these migrations can vary depending on the species and environmental factors, such as temperature and food availability.
Feeding Behavior of Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
Food Sources
Saltwater bottom feeder fish have an omnivorous diet and feed on a wide range of food sources. They scavenge for decaying organic matter, detritus, small invertebrates, and plant material present on the ocean floor. Some species may also consume small fish or crustaceans that they encounter while foraging.
Foraging Techniques
These fish employ different foraging techniques depending on their specific adaptations and the available food sources. Some may use their jaws to sift through the substrate, while others may use their feeding appendages or mouths to pick up food particles. Certain species can even create small disturbances in the sand or mud to uncover hidden prey.
Competition for Food
Competition for food resources is a factor that influences the behavior and success of saltwater bottom feeder fish. In areas where multiple species coexist, there may be competition for limited food sources, leading to adaptations such as specialized feeding techniques or occupying different microhabitats. This competition helps maintain a balance within the ecosystem and promotes species diversity.
Carnivorous or Herbivorous
While many saltwater bottom feeder fish are omnivorous, certain species have a preference for either carnivorous or herbivorous diets. Carnivorous species primarily feed on small invertebrates or other fish, while herbivorous species consume algae and plant material. This diversity in feeding preferences contributes to the overall stability and functioning of the marine ecosystem.
Role in Marine Ecosystem
Cleaners of the Ocean Floor
One of the significant roles played by saltwater bottom feeder fish is their function as “cleaners” of the ocean floor. They consume decaying organic matter and detritus, preventing the build-up of waste materials and promoting nutrient recycling. By removing this debris, they contribute to the overall cleanliness and health of the marine environment.
Recyclers of Nutrients
Saltwater bottom feeder fish aid in the recycling of nutrients, as they digest and excrete organic matter from the ocean floor. The nutrients released back into the water column enhance the availability of vital elements needed for the growth of microscopic organisms, which then serve as food for other marine organisms. This recycling process ensures that nutrients are continuously cycled through the ecosystem.
Prey for Predators
As bottom-dwelling organisms, saltwater bottom feeder fish serve as a crucial food source for larger predators in the marine ecosystem. They form an essential link in the food chain, transferring energy from the lower levels to higher trophic levels. Their abundance and availability contribute to the sustenance of various fish, mammals, and birds that rely on them for their survival.
Indicators of Environmental Health
The presence and abundance of saltwater bottom feeder fish can serve as indicators of the overall health and condition of the marine environment. By monitoring their populations, scientists can gain insights into the effects of pollution, habitat degradation, or overfishing. Changes in the abundance or behavior of these fish can signify potential imbalances or disturbances within the ecosystem.

Common Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish Species
Catfish
Catfish, known for their distinct barbels or “whiskers,” are a common type of saltwater bottom feeder fish. They are found in coastal areas across the world and play a vital role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. Catfish possess a voracious appetite, feeding on a variety of food sources, including small fish, invertebrates, and algae.
Triggerfish
Triggerfish are another well-known species of saltwater bottom feeders. They are known for their strong jaws and teeth, which allow them to crush and access the hard shells of invertebrates such as crabs and snails. Triggerfish play a crucial role in controlling the population of these organisms and contribute to the overall health of coral reef ecosystems.
Flounder
Flounder are unique saltwater bottom feeder fish with both eyes on one side of their body. Their positioning enables them to camouflage effectively, blending into the sandy or muddy substrate. Flounder rely on their ambush hunting technique, lying in wait for passing prey such as small fish or crustaceans. Their ability to mimic their surroundings allows them to catch prey by surprise.
Gobies
Gobies, with their vibrant colors and small size, are another group of saltwater bottom feeder fish. They can be found in a wide range of habitats, including coral reefs, mangroves, and coastal areas. Gobies often possess specialized mouth structures that allow them to sift through sand or pick up food particles from the bottom.
Parrotfish
Parrotfish, characterized by their beak-like mouth and vibrant coloration, are prominent members of the saltwater bottom feeder group. They play a crucial role in the health of coral reefs by grazing on algae and other organic material that can smother and damage the reef structure. Parrotfish also contribute to the production of sand, as they ingest coral and excrete fine particles.
Behavior and Reproduction
Social Structure
The social structure of saltwater bottom feeder fish varies among species. Some species exhibit solitary behavior, while others form small groups or schools. The social structure often depends on the specific ecological requirements and prey availability of the species in question. It is not uncommon to find species that are territorial, defending their feeding areas or preferred habitats.
Breeding and Spawning
The breeding and spawning behavior of saltwater bottom feeder fish typically involves unique adaptations. Many species engage in elaborate courtship rituals to attract mates, while others simply release their eggs and sperm into the water column. Some species may deposit their eggs within specific habitats, such as nests or burrows, to provide protection and increase the chances of survival for their offspring.
Parental Care
Parental care in saltwater bottom feeder fish can vary significantly. Some species exhibit little to no parental care, with the fertilized eggs and subsequent larvae left to fend for themselves. In contrast, other species may display impressive care, with parents guarding their nests, aerating the eggs, or even carrying the developing young within their mouths.
Survival Strategies
To survive in the challenging marine environment, saltwater bottom feeder fish have developed various strategies. Their specialized body shapes and camouflage techniques aid in avoiding predators, while their feeding adaptations maximize their ability to find and consume food sources. Some species may also possess unique physiological adaptations, such as the ability to tolerate low oxygen conditions or extreme temperatures.
Challenges Faced by Saltwater Bottom Feeder Fish
Overfishing
One of the significant challenges faced by saltwater bottom feeder fish is overfishing. The high demand for these species, either for human consumption or the aquarium trade, has led to unsustainable fishing practices and depleted populations. Overfishing disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, affecting not only the bottom feeder fish but also other species that rely on them for food.
Habitat Destruction
The destruction of coastal habitats, such as mangroves and coral reefs, poses a significant threat to saltwater bottom feeder fish. These habitats provide essential feeding and breeding grounds for these species, and their destruction can disrupt their life cycles and reduce available resources. Coastal development, pollution, and destructive fishing practices all contribute to habitat degradation.
Pollution and Contaminants
Pollution, including runoff from land-based activities and discharge from industrial sources, negatively impacts saltwater bottom feeder fish. Accumulation of contaminants, such as heavy metals or chemical pollutants, can impair their reproductive abilities, compromise their health, and even lead to population declines. Pollution mitigation strategies are crucial to ensure the long-term survival of these species.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to saltwater bottom feeder fish and their habitats. Rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification, and sea-level rise can disrupt the delicate ecological balance on which these species rely. Changes in water conditions can impact their feeding behavior, reproductive success, and overall survival. Adaptation and mitigation efforts are crucial to protect these vulnerable species.
Conservation Efforts and Management
Protected Areas and Reserves
The establishment of protected areas and marine reserves is a vital conservation tool for saltwater bottom feeder fish. These designated zones offer a sanctuary for these species, allowing them to feed, breed, and thrive undisturbed. By limiting human activities in these areas, such as fishing or development, these protected areas provide a safe haven for these vital members of the marine ecosystem.
Fishing Regulations
Implementing and enforcing fishing regulations is essential in managing saltwater bottom feeder fish populations sustainably. These regulations can include size limits, bag limits, closed seasons, and gear restrictions to ensure that fishing practices do not lead to overexploitation. Balancing the needs of fishing communities and the long-term health of these fish populations is crucial for effective management.
Habitat Restoration
Efforts to restore and protect critical habitats, such as coral reefs and mangroves, are essential for the survival of saltwater bottom feeder fish. Restoration projects focus on reducing pollution, replanting damaged areas, and promoting sustainable practices to enhance the health and resilience of these ecosystems. Restored habitats provide more abundant food sources and improved breeding grounds for these species.
Education and Awareness
Educating the public about the importance of saltwater bottom feeder fish and their ecological role is crucial for their conservation. Increasing awareness about the threats they face and promoting sustainable practices, such as responsible fishing and reducing pollution, can help protect their habitats and preserve their populations. Education plays a vital role in fostering a sense of stewardship for these unique creatures.
Conclusion
Saltwater bottom feeder fish are essential members of the marine ecosystem, playing vital roles in maintaining balance and contributing to the overall health of our oceans. Their physical features, feeding behavior, and adaptations have allowed them to thrive in specific habitats and occupy a niche that supports numerous other species. However, they face numerous challenges, including overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and the impacts of climate change. Conservation efforts, such as protected areas, fishing regulations, habitat restoration, and education, are crucial for ensuring the long-term survival of these valuable species. By appreciating and safeguarding saltwater bottom feeder fish, we can contribute to the conservation of our oceans and promote a healthier and more sustainable future for all.