Contents
- 1. Types of Fish Feed
- 2. Understanding Fish Dietary Requirements
- 3. Determining the Right Amount of Feed
- 4. Implementing Feeding Techniques
- 5. Fish Feeding Strategies
- 6. Overcoming Feeding Challenges
- 7. Environmental Enrichment for Feeding
- 8. Monitoring Fish Feeding Response
- 9. Special Considerations for Aquaponics
- 10. Research and Innovations in Fish Feeding
Are you a fish enthusiast looking to enhance your feeding techniques? Look no further! In this article, we explore the innovative world of directional fish feeders, a game-changer in the fishkeeping community. Discover how these devices revolutionize feeding time, ensuring your underwater friends receive their meals precisely and efficiently. From adjustable feeding angles to accurate portion control, this technology offers a convenient solution to enhance fish feeding in your aquarium. Get ready to take your fish care skills to the next level with these exciting advancements!
1. Types of Fish Feed
1.1 Dry Pellets
Dry pellets are one of the most common types of fish feed available on the market. These pellets are compacted and dried, providing a convenient and long-lasting option for feeding your fish. Dry pellets come in various sizes to accommodate different fish species and their feeding habits. They typically contain a balanced blend of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and essential nutrients to support optimal fish growth and health.
1.2 Live Food
Live food, such as brine shrimp, daphnia, and bloodworms, can be a great option for adding variety to your fish’s diet. These live organisms are rich in nutrients and closely mimic the natural prey of many fish species. Feeding live food can stimulate your fish’s natural hunting instincts and provide mental stimulation. However, it is important to ensure that the live food you offer is clean and free from parasites or diseases that could harm your fish.
1.3 Frozen Food
Frozen food is another popular choice for fish feeding. It offers the convenience of long shelf life while still providing the nutritional benefits of live food. Frozen foods like brine shrimp, mysis shrimp, and spirulina can be easily thawed and fed to your fish. They retain most of their nutritional value and are a practical option for fish owners who want to provide a varied diet for their aquatic pets.
1.4 Flakes
Fish flakes are a staple option for many aquarium fish. They are made of a mixture of ingredients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals, all pressed into thin, flake-like shapes. Flakes are particularly suitable for small fish species that have tiny mouths or swim close to the water surface. They offer a balanced diet and are easily consumed by fish. However, it is important to ensure that the flakes are fresh and haven’t lost their nutritional value.
2. Understanding Fish Dietary Requirements
2.1 Essential Nutrients
Fish, like any other living organism, require a range of essential nutrients to maintain optimal health. Proteins are crucial for growth and tissue repair, while carbohydrates provide energy. Fats are necessary for energy storage and insulation, and micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals play vital roles in various physiological processes. Understanding the specific dietary requirements of your fish species is essential for providing a balanced and nutritious diet.
2.2 Protein Levels
Protein is a vital component of a fish’s diet as it provides the necessary amino acids for growth and development. Different fish species have varying protein requirements, typically ranging from 25% to 50% of their diet. Commercial fish feeds usually state the protein content on the packaging, making it easier for fish owners to select an appropriate feed for their specific species.
2.3 Carbohydrates and Fats
Carbohydrates and fats are essential sources of energy for fish. While carbohydrates are not as prominent in a fish’s diet compared to proteins, they still provide crucial energy reserves. Fats are an important component of fish feed as they supply concentrated energy and are necessary for maintaining healthy skin and providing insulation. It is important to strike a balance between carbohydrates and fats in the diet to prevent obesity or malnutrition in fish.
2.4 Micronutrients
Micronutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, play essential roles in various physiological processes, including metabolism and immune system function. These nutrients are required in smaller quantities compared to macronutrients like proteins and carbohydrates but are equally important. Fish feeds are often supplemented with a range of vitamins and minerals to ensure that the dietary requirements of fish are met.
2.5 Feeding Frequency
Determining the appropriate feeding frequency for your fish depends on several factors, such as the species, size, and age of your fish. Some fish, like herbivores, may require frequent feedings throughout the day, while others, like carnivores, may prefer fewer but more substantial meals. Observing your fish’s behavior and monitoring their body condition can help you determine the right feeding frequency. It is important not to overfeed, as this can lead to water quality issues and obesity in fish.
3. Determining the Right Amount of Feed
3.1 Fish Size and Body Condition
The size and body condition of your fish play a significant role in determining the right amount of feed. Smaller fish generally require less feed compared to larger fish. It is important to feed your fish an amount that they can consume within a few minutes, ensuring that no excess feed is left uneaten to avoid polluting the water. Monitoring your fish’s body condition and adjusting the feeding amount accordingly can help prevent underfeeding or overfeeding.
3.2 Water Temperature
Water temperature can influence a fish’s metabolic rate and therefore impact their feeding habits. Warmer water temperatures generally increase a fish’s appetite, while colder temperatures may decrease their feeding activity. It is important to consider the optimal temperature range for your fish species and adjust their feeding accordingly. During colder months, fish may require less feed, while in warmer months, their food intake may increase.
3.3 Water Quality
Maintaining good water quality is crucial for the overall health of your fish and their ability to feed optimally. Poor water quality can stress fish and lead to decreased feeding activity. It is essential to regularly test the water parameters, such as ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and pH, to ensure they are within the appropriate range. If the water quality is compromised, it can affect your fish’s appetite, digestion, and overall well-being.
3.4 Species-specific Guidelines
Different fish species have varying dietary requirements and feeding habits. It is important to research and understand the specific needs of your fish species. Some fish are herbivores and require a predominantly plant-based diet, while others are carnivores and require a diet rich in animal proteins. Consulting species-specific feeding guidelines can help you determine the appropriate feed type and feeding frequency for your fish.
4. Implementing Feeding Techniques
4.1 Hand Feeding
Hand feeding involves directly offering food to your fish using your hand or a feeding tool. This technique allows for close interaction with your fish and can be particularly beneficial for building trust and observing their feeding behavior. It is important to ensure that your hands or any feeding tools are clean to avoid introducing contaminants into the tank. Hand feeding can be a great way to bond with your fish and make their feeding experience more engaging.
4.2 Automatic Feeders
Automatic feeders are devices that allow you to schedule and automate the feeding process for your fish. These feeders dispense a predetermined amount of feed at set intervals throughout the day. Automatic feeders can be particularly useful when you are away from home or have a busy schedule. They ensure that your fish are consistently fed even in your absence, maintaining their health and well-being.
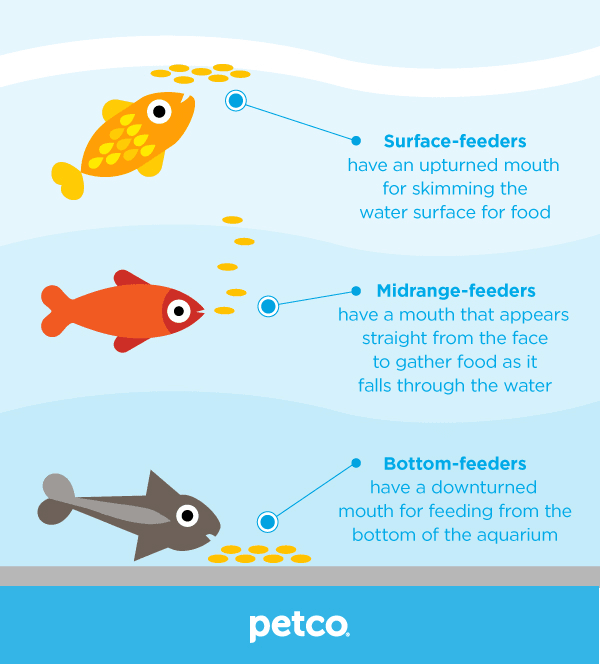
4.3 Surface Feeders
Some fish species, such as bettas or guppies, prefer feeding at the water surface. These surface feeders rely on their ability to snatch prey from the water’s surface. Offering floating pellets or flakes that stay on the water surface allows these fish to exhibit their natural feeding behavior. Surface feeders can add excitement and enrichment to your aquarium while also ensuring that the fish receive their feed effectively.
4.4 Bottom Feeders
Bottom feeders, such as catfish or loaches, have specialized feeding adaptations that allow them to scavenge and feed from the substrate or tank bottom. Providing sinking pellets or wafer-like feeds allows these fish to display their natural behavior while receiving adequate nutrition. Observing your bottom feeders during feeding can be fascinating, as they use their barbels or mouths to search and consume the feed on the tank bottom.
4.5 Feeding Rings
Feeding rings are floating devices that can be placed on the water surface to confine the fish’s feed to a specific area. These rings prevent the feed from scattering throughout the tank, making it easier for fish to locate and consume their food. Feeding rings are particularly useful in community tanks where multiple fish species with different feeding habits coexist. They ensure that each fish has access to their feed and prevent feeding competition.
5. Fish Feeding Strategies
5.1 Balanced Feeding
A balanced feeding strategy involves providing a varied and nutritionally complete diet to your fish. This strategy ensures that all the essential nutrients required by your fish are met, preventing any nutritional deficiencies. Combining different types of feed, such as dry pellets, frozen food, and live food, can offer a diverse range of nutrients while keeping your fish engaged and interested in feeding.
5.2 Sequential Feeding
Sequential feeding involves offering different types of feed in a specific order or sequence. This strategy allows you to target the nutritional needs and feeding preferences of your fish species. For example, you can start with dry pellets, followed by live food, and finish with frozen food. Sequential feeding can provide a well-rounded diet while stimulating your fish’s natural feeding instincts.
5.3 Daytime vs. Nighttime Feeding
Observing your fish’s feeding behavior can help determine whether they prefer daytime or nighttime feeding. Some fish species are more active and receptive to feeding during the daytime, while others are nocturnal and prefer feeding at night. Adjusting the feeding schedule to align with your fish’s natural behavior can enhance their feeding response and ensure that they consume their feed effectively.
5.4 Feeding Behavior Observation
Regularly observing your fish’s behavior during feeding can provide valuable insights into their health and well-being. Healthy fish will actively pursue and consume their feed, displaying enthusiasm and energy. On the other hand, if you notice any changes in their feeding behavior, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, or excessive aggression during feeding, it could indicate underlying health issues. Timely observation and addressing any feeding behavior changes can help maintain the overall health of your fish.
6. Overcoming Feeding Challenges
6.1 Shy or Skittish Fish
Some fish species may exhibit shy or skittish behavior, making it challenging for them to feed in the presence of humans or other tank mates. To overcome this challenge, it is important to create a calm and quiet feeding environment. Turning off bright lights, minimizing activity near the tank during feeding, and using feeding rings or feeding tubes can provide a more secure and comfortable feeding experience for shy or skittish fish.
6.2 Aggressive Feeders
Aggressive feeders, such as cichlids or larger predatory fish, may exhibit territorial behavior during feeding. This can lead to feeding competition and potential aggression among tank mates. To address this challenge, ensuring sufficient feeding spots and providing distraction or hiding places, such as caves or plants, can help reduce aggression and ensure that all fish have access to their feed.
6.3 Floating vs. Sinking Feed
Choosing the right type of feed based on your fish’s feeding habits is crucial. Some fish prefer feed that floats on the water surface, while others may be more inclined to consume sinking or bottom-dwelling feed. Observing your fish’s feeding behavior can help determine their preference, and providing the appropriate feed type can enhance their feeding response and prevent any feed wastage.
6.4 Feeding Competition
Feeding competition can arise when multiple fish species with different feeding habits coexist in the same tank. Aggressive or dominant fish may consume most of the feed, leaving others at a disadvantage. To overcome this challenge, offering feed in multiple feeding spots or using feeding rings can help distribute the feed evenly and prevent any one fish from monopolizing the food source.
6.5 Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can occur when fish are not provided with a balanced and varied diet. Insufficient intake of essential nutrients can lead to stunted growth, weakened immune systems, and various health issues. To address this challenge, it is important to research and understand the specific dietary requirements of your fish species. Supplementing their diet with appropriate vitamins and minerals or consulting with a veterinarian can help prevent nutritional deficiencies.

7. Environmental Enrichment for Feeding
7.1 Feeding Toys and Devices
Adding feeding toys or devices to your aquarium can provide environmental enrichment for your fish during feeding. These toys can include floating puzzles or food dispensers that require fish to work for their food. They stimulate natural foraging behaviors and mental stimulation, promoting a more active and engaged feeding experience. Feeding toys and devices can be particularly beneficial for highly intelligent fish species.
7.2 Variability in Feeding Locations
Creating variability in feeding locations can simulate the natural feeding environments of fish. This can be achieved by placing feed in different areas of the tank, such as near plants, rocks, or caves. Changing the location of the feed can encourage fish to explore their environment and exhibit their natural feeding behaviors, promoting a more engaging and enriching feeding experience.
7.3 Natural Feeding Simulations
Simulating natural feeding simulations can provide a more realistic and enriching feeding experience for your fish. For example, you can release live prey into the tank to allow your fish to exhibit their hunting instincts and engage in natural feeding behaviors. However, it is important to ensure that the live prey is free from parasites or diseases to prevent any harm to your fish.
7.4 Light and Temperature Control
Controlling the lighting and temperature conditions during feeding can influence your fish’s feeding response. For example, dimming the lights or providing a gentle moonlight simulation can mimic a natural feeding environment for nocturnal fish. Similarly, maintaining the appropriate water temperature can enhance your fish’s metabolic activity and appetite. Ensuring that the tank environment closely resembles their natural habitat can optimize their feeding experience.
8. Monitoring Fish Feeding Response
8.1 Visual Assessment
Regularly visually assessing your fish during feeding can provide valuable information about their health and feeding habits. Healthy fish will actively pursue their feed, display vibrant colors, and show enthusiasm during feeding. Any changes in their behavior, such as loss of appetite, lethargy, or clamped fins, could indicate underlying health issues that require attention. Visual assessment can help you identify any potential problems and take appropriate action.
8.2 Weight Monitoring
Monitoring your fish’s weight can be an effective way to assess their feeding response and overall health. Consistent weight gain indicates a healthy feeding response, while sudden weight loss or stagnation may indicate issues with feeding or underlying health problems. Using a digital scale or monitoring changes in body shape and size can help you track your fish’s weight and adjust their feeding accordingly.
8.3 Waste Evaluation
Evaluating the waste produced by your fish can provide insights into their feeding response and digestion. Healthy fish produce well-formed, small amounts of waste that quickly break down in the tank. Excessive or abnormal waste, such as unusual color or consistency, could indicate overfeeding or digestive issues. Regularly monitoring and assessing the waste produced by your fish can help you adjust their feeding and ensure their overall well-being.
8.4 Behavioral Changes
Observing any behavioral changes during or after feeding can provide valuable information about your fish’s feeding response. Healthy fish will exhibit natural feeding behaviors, such as actively pursuing their feed or searching for food on the tank bottom. Any sudden changes, such as loss of interest in feeding, aggression during feeding, or avoidance of certain feed types, could indicate an underlying health issue or feeding challenge that requires attention.
9. Special Considerations for Aquaponics
9.1 Balancing Fish and Plant Nutrition
Aquaponics combines fish farming and hydroponics, creating a symbiotic system where fish waste provides the nutrients for plant growth. Balancing fish and plant nutrition is essential to maintain the health and productivity of both components. Ensuring that the fish receive a nutritionally complete diet and selecting appropriate fish species that produce compatible waste for the plants can optimize the nutrient cycle in aquaponics systems.
9.2 Feed Conversion Ratios
Feed conversion ratios (FCR) in aquaponics refer to the amount of fish feed required to produce a given weight of fish. Optimizing FCR is important to maximize the efficiency and sustainability of the system. Lower FCR indicates that the fish are converting feed into muscle mass effectively, while higher FCR may indicate inefficiencies in the system. Monitoring FCR and adjusting the feed amount and type can help optimize fish growth and minimize waste.
9.3 Water Quality Impact
In aquaponics, the fish waste provides nutrients for plant growth, but it can also impact water quality if not properly managed. Excessive fish feed or inefficient filtration can lead to elevated ammonia, nitrite, or nitrate levels, which can be harmful to both fish and plants. Monitoring water quality parameters regularly and implementing appropriate filtration systems or biofilters can help maintain optimal water conditions for both fish and plant health.
9.4 Organic Feeding Approaches
Organic feeding approaches in aquaponics aim to minimize the use of synthetic or chemical-based feeds and focus on using natural, organic feed sources. This can include incorporating live food, such as worms or insects, into the fish’s diet or growing organic plant-based feeds within the aquaponics system. Organic feeding approaches promote sustainability, reduce environmental impacts, and align with organic farming principles.
10. Research and Innovations in Fish Feeding
10.1 Genetic Modification of Feeds
Genetic modification of fish feeds involves incorporating specific genes or modifying the nutritional composition of feed ingredients to enhance the growth, health, or nutrient utilization of fish. Research in this field aims to develop feeds that optimize fish growth and health while reducing the environmental impact. Genetic modification of feeds remains a topic of debate and requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
10.2 Sustainable Feed Ingredients
Sustainable feed ingredients are gaining importance in fish feeding practices. The use of alternative protein sources, such as insects, algae, or single-cell proteins, aims to reduce the reliance on traditional fishmeal and fish oil derived from wild-caught fish stocks. Sustainable feed ingredients promote resource efficiency, minimize the environmental impact of fish farming, and contribute to the long-term sustainability of the aquaculture industry.
10.3 Automated Feeding Systems
Automated feeding systems are continually evolving and becoming more advanced, offering increased precision and control over the feeding process. These systems can be programmed to dispense feed at specific times and in predetermined quantities, ensuring consistency and minimizing wastage. Automated feeders can also be integrated with monitoring systems to track feeding response and adjust feed amounts accordingly, optimizing fish growth and health.
10.4 Nutrigenomics and Personalized Feeds
Nutrigenomics explores the interaction between nutrition and gene expression in fish. This field of study aims to develop personalized feeding approaches based on individual fish’s genetic profiles and nutritional requirements. Personalized feeds can optimize nutrient utilization, growth, and overall health based on the specific genetic traits and needs of each fish. Nutrigenomics has the potential to revolutionize fish feeding practices and create tailored nutritional solutions.