Contents
- Diagnostic Process for Autism
- 2. Types of Autism Testing
- 3. Costs Involved in Autism Testing
- 4. Insurance Coverage for Autism Testing
- 5. Out-of-Pocket Expenses for Autism Testing
- 6. Factors Affecting Autism Testing Costs
- 7. Cost of Autism Screening
- 8. Cost of Comprehensive Autism Assessment
- 9. Additional Costs for Genetic Testing
- 10. Financial Aid and Support Programs
Autism, a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication and social interactions, can often go undiagnosed for years. If you suspect that you or a loved one might have Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and are wondering about the cost associated with getting tested, you’re in the right place. In this article, we will explore the various factors that can influence the cost of autism testing and provide you with a comprehensive overview of what to expect when seeking an evaluation.
Diagnostic Process for Autism
1.1 Screening for Autism
The diagnostic process for autism typically begins with screening. Screening tools and instruments are used to identify individuals who may exhibit signs of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). These tools are designed to assess a variety of developmental areas, including social interaction, communication, and behavior. Screening is often conducted by healthcare professionals, such as pediatricians or psychologists, in various settings such as clinics, schools, or early intervention programs.
1.2 Comprehensive Assessment
After a positive screening result, a comprehensive assessment is conducted to gather more detailed information about an individual’s strengths, challenges, and developmental history. This assessment involves a thorough evaluation by a team of professionals, which may include psychologists, psychiatrists, speech and language therapists, and occupational therapists. The goal of the assessment is to determine whether the individual meets the diagnostic criteria for autism.
1.3 Multi-Disciplinary Evaluation
As part of the diagnostic process, a multi-disciplinary evaluation is often recommended. This involves input from professionals representing various disciplines, such as psychology, medicine, genetics, and education. The evaluation combines information from different sources to provide a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s unique needs and challenges. It may include observations, interviews, and assessments conducted by different professionals with relevant expertise.
1.4 Diagnostic Criteria
The final step in the diagnostic process for autism involves assessing whether an individual meets the diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). The DSM-5 provides specific criteria for the diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder, including the presence of social communication deficits, restricted and repetitive behaviors, and the early onset of symptoms. A thorough review of the individual’s assessment results and developmental history is used to determine if they meet these criteria.
2. Types of Autism Testing
2.1 Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Diagnostic Tools
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnostic tools are specifically designed to assess and evaluate individuals suspected of having autism. These tools may include rating scales, questionnaires, and structured interviews that gather information about the individual’s social and communication skills, behavior patterns, and sensory sensitivities. Some commonly used diagnostic tools for ASD include the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R).
2.2 Medical Evaluation
A medical evaluation is an important component of autism testing. It involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional, such as a pediatrician or neurologist, to rule out any physical conditions or medical issues that may be contributing to the individual’s symptoms. The medical evaluation may include a physical examination, review of medical history, and additional tests, such as blood tests or neuroimaging, if necessary.
2.3 Genetic Testing
Genetic testing may be recommended as part of the autism diagnostic process, particularly in cases where there is a family history of autism or other genetic conditions. Genetic tests can help identify specific gene mutations or chromosomal abnormalities that may be associated with autism spectrum disorder. Testing can be performed on a blood sample or other tissue samples, and results can provide valuable information about the individual’s diagnosis and potential treatment options.
2.4 Psychological Testing
Psychological testing plays a vital role in the assessment of autism. It involves the administration of standardized tests and assessments to gather information about the individual’s cognitive abilities, language skills, social-emotional functioning, and behavioral patterns. These tests are conducted by licensed psychologists or neuropsychologists and can provide valuable insights into the individual’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall psychological functioning.
2.5 Speech and Language Assessments
Speech and language assessments are conducted by speech-language pathologists (SLPs) and focus on evaluating an individual’s communication skills. These assessments may involve observing the individual’s speech production, language comprehension, and use of nonverbal communication. The results of these assessments help determine the individual’s speech and language abilities and any areas that may require intervention or support.
2.6 Occupational Therapy Assessments
Occupational therapy assessments evaluate an individual’s sensory processing, motor skills, and daily living skills. Occupational therapists use standardized assessments and observations to assess the individual’s ability to engage in various activities and tasks. These assessments can help identify areas of difficulty and guide the development of individualized intervention plans to support the individual in their daily activities and routines.
2.7 Behavioral Assessments
Behavioral assessments are conducted to gather information about an individual’s behavior patterns, social skills, and response to different situations. These assessments are typically conducted by behavior analysts or psychologists trained in behavioral analysis. They may involve direct observations, interviews with caregivers, and the use of behavior rating scales or checklists. The results of behavioral assessments inform the development of behavior intervention plans and strategies to support individuals with autism.
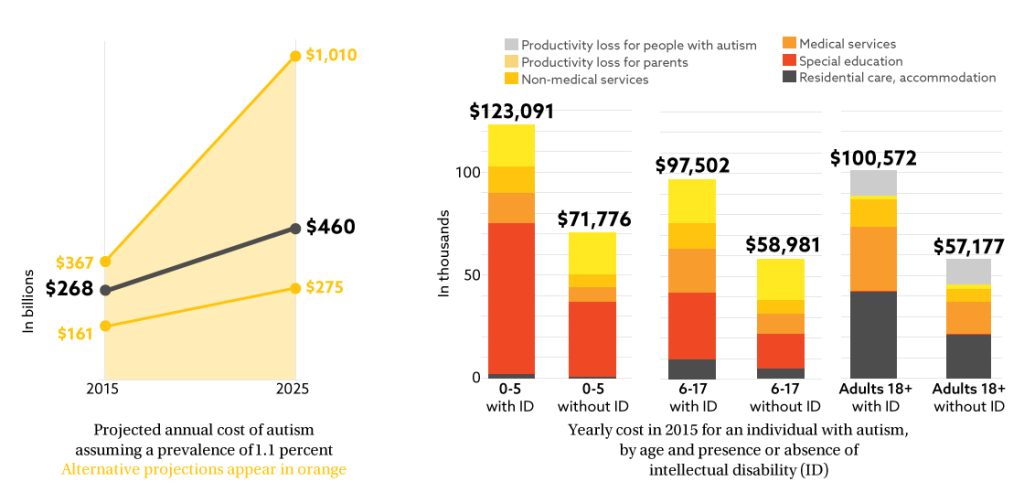
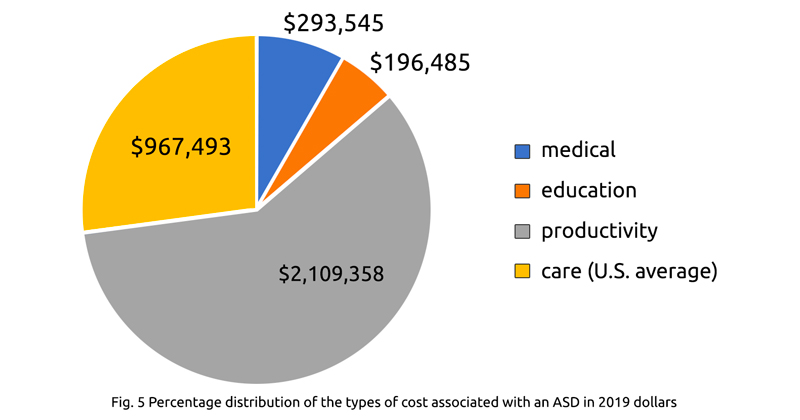
3. Costs Involved in Autism Testing
3.1 Insurance Coverage
One of the important factors to consider when undergoing autism testing is insurance coverage. Depending on the type of insurance plan you have, certain diagnostic procedures and assessments may be covered. Private health insurance providers often offer coverage for autism testing, but the extent of coverage may vary. It is essential to review your insurance policy and contact your insurance provider to determine which specific assessments and treatments are covered and to what extent.
3.2 Out-of-Pocket Expenses
In cases where insurance coverage is limited or unavailable, individuals and their families may need to bear the costs of autism testing themselves. These out-of-pocket expenses can include screening costs, assessment fees, and costs associated with additional testing or evaluations. It is crucial to be aware of these potential expenses and plan accordingly to ensure access to necessary evaluations and assessments.
3.3 Screening Costs
The cost of autism screening can vary depending on the setting, healthcare provider, and specific screening tools used. Screening costs may range from a nominal fee to several hundred dollars. It is advisable to consult with healthcare professionals or autism-specific organizations to inquire about screening costs and any available financial assistance programs.
3.4 Comprehensive Assessment Costs
Comprehensive assessments, which involve a team of professionals from different disciplines, generally incur higher costs compared to screening. The fees for comprehensive assessments can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the case, the number of professionals involved, and the duration of the assessments. These costs typically cover the professional fees for each specialist involved and any additional testing materials or equipment that may be required.
3.5 Genetic Testing Costs
If genetic testing is recommended as part of the autism diagnostic process, there may be additional costs associated with it. The cost of genetic testing varies depending on the type of test, the laboratory used, and whether the testing is covered by insurance. It is important to discuss the potential costs of genetic testing with the healthcare provider and check with the insurance company for coverage and reimbursement policies.
3.6 Psychological Testing Costs
Psychological testing costs can also contribute to the overall expenses of autism testing. The fees for psychological testing may vary depending on the complexity and duration of the assessments, as well as the expertise and qualifications of the licensed psychologist or neuropsychologist conducting the tests. It is advisable to discuss these costs with the healthcare provider and inquire about any available financial assistance programs or sliding scale fees.
3.7 Speech and Language Assessment Costs
Speech and language assessments are typically conducted by licensed speech-language pathologists (SLPs). The costs of these assessments may vary depending on the provider, location, and duration of the evaluation. It is recommended to consult with SLPs or speech therapy clinics to inquire about the fees involved in speech and language assessments and any potential funding options or assistance programs.
3.8 Occupational Therapy Assessment Costs
Occupational therapy assessments assess an individual’s sensory processing, motor skills, and daily living abilities. The costs of these assessments can vary depending on the healthcare provider, location, and duration of the evaluations. It is advisable to contact occupational therapy clinics or providers to discuss assessment costs and explore any available financial aid or support programs.
3.9 Behavioral Assessment Costs
Behavioral assessments are conducted by behavior analysts or psychologists specializing in behavioral analysis. The costs of these assessments can vary based on the complexity of the assessment, the number of professionals involved, and the duration of the evaluation. It is important to inquire about the fees for behavioral assessments with qualified professionals and seek information on financial assistance or sliding scale payment options if needed.
3.10 Variation in Costs
It is important to note that the costs involved in autism testing can vary significantly depending on various factors such as geographical location, healthcare provider rates, the complexity of the case, additional services required, and insurance coverage. Therefore, it is advisable to obtain estimates and discuss costs with healthcare professionals and insurance providers beforehand to budget and plan accordingly.
4. Insurance Coverage for Autism Testing

4.1 Coverage under Private Health Insurance
Many private health insurance plans cover autism testing to some extent. However, the coverage offered may vary depending on the specific insurance provider, plan, and local regulations. Some insurance plans may cover certain diagnostic procedures, assessments, or therapy services related to autism, while others may have limitations or exclusions. It is crucial to review the insurance policy’s terms and conditions, including any applicable copayments, deductibles, or coverage limits, and seek clarification from the insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage for autism testing.
4.2 Coverage under Government Programs (Medicaid, Medicare)
In some countries, government programs such as Medicaid or Medicare may provide coverage for autism testing. These programs are typically targeted at individuals and families with low-income or specific eligibility criteria. Coverage under government programs for autism testing may vary, and it is advisable to contact the relevant agency or program to inquire about the covered services, eligibility requirements, and application procedures.
4.3 Coverage Limitations and Criteria
While private health insurance and government programs may offer coverage for autism testing, it is essential to be aware of any coverage limitations or criteria that need to be met. These limitations may include age restrictions, requirements for prior authorization, the need for medical necessity, or limitations on the number of assessments or therapy sessions covered. Understanding the specific limitations and criteria is crucial to ensure access to appropriate coverage and avoid unexpected expenses.
4.4 Reimbursement Process
When seeking autism testing covered by insurance, it is essential to understand the reimbursement process. This process typically involves submitting a claim or bill for the services rendered to the insurance company. The insurance company will review the claim and determine the eligible reimbursement amount based on the coverage and policy terms. It is advisable to keep detailed records and documentation of all testing-related expenses and consult with the insurance provider to understand the specific reimbursement process and requirements.
4.5 Prior Authorization
In some cases, insurance coverage for certain autism diagnostic procedures or assessments may require prior authorization. Prior authorization involves obtaining approval from the insurance company before undergoing the specified services. The process typically involves submitting detailed information about the individual’s condition, the recommended assessments, and the medical necessity for the requested services. It is crucial to inquire about any prior authorization requirements and procedures with the insurance provider to ensure smooth and timely access to covered services.
5. Out-of-Pocket Expenses for Autism Testing
5.1 Cost Range of Autism Testing
The cost range of autism testing can vary greatly depending on several factors, such as the type and number of assessments required, the professionals involved, and the geographic location. Out-of-pocket expenses for autism testing can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. It is advisable to obtain estimates from healthcare professionals or diagnostic centers to understand the potential out-of-pocket costs involved in the specific case.
5.2 Diagnostic Centers and Specialists
Diagnostic centers and specialists play a crucial role in autism testing. The fees charged by diagnostic centers and specialists for their services can vary significantly depending on factors such as location, reputation, expertise, and demand. It is advisable to research and compare the fees charged by different centers or specialists to ensure the best quality evaluation and assessment services within a reasonable cost range.

5.3 Additional Services
In addition to the core assessment and diagnostic procedures, individuals with autism may require additional services, interventions, or therapies to support their development and address specific needs. These additional services, such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, or applied behavior analysis (ABA) therapy, can entail additional costs. It is important to consider these potential expenses when budgeting for autism testing and ongoing treatment.
5.4 Travel and Accommodation Costs
In some cases, individuals may need to travel to access specialized diagnostic centers or professionals with expertise in autism assessment. Traveling for autism testing can add to the overall costs, including transportation expenses, accommodation costs, and potential meals or incidental expenses. Planning and budgeting for these additional costs is essential, particularly for individuals living in areas with limited local autism assessment resources.
5.5 Financial Assistance Programs
To alleviate the burden of out-of-pocket expenses, individuals and families may explore financial assistance programs specifically designed to support individuals with autism. These programs can provide financial aid, grants, or scholarships that can help offset the costs of autism testing and related services. It is advisable to research and inquire about such programs through autism-specific organizations, community resources, or governmental agencies to explore potential financial assistance options.
6. Factors Affecting Autism Testing Costs
6.1 Geographical Location
Geographical location can significantly impact the costs associated with autism testing. Diagnostic services and professionals in urban areas or regions with a higher cost of living may charge higher fees compared to those in rural or less affluent areas. Consideration should be given to the availability and accessibility of diagnostic services in different locations, as travel costs may also come into play.
6.2 Healthcare Provider Rates
Healthcare provider rates can vary based on factors such as experience, qualifications, and demand for services. Specialists or centers with extensive expertise in autism assessment may charge higher fees compared to generalist providers. It is advisable to research and compare the rates charged by different healthcare providers while considering their qualifications and expertise in autism assessment.
6.3 Complexity of the Case
The complexity of an individual’s presentation can impact the costs of autism testing. Cases that require extensive assessment, additional specialized consultations, or genetic testing may incur higher costs compared to simpler cases. The number of professionals involved and the duration of assessments may also contribute to increased costs. The complexity of the case should be discussed with healthcare professionals to understand the potential costs involved.
6.4 Additional Services Required
The need for additional services, interventions, or therapies can affect the overall costs of autism testing. Some individuals may require speech therapy, occupational therapy, or ABA therapy as part of their treatment plan. The costs associated with these additional services should be considered when budgeting for autism testing and ongoing support.

6.5 Insurance Plans and Coverage
Insurance plans and the extent of coverage available can have a significant impact on autism testing costs. The coverage offered by different insurance providers and plans may vary, and some diagnostic procedures or assessments may not be covered at all. Understanding the specific coverage and limitations of the insurance plan is important to assess the potential out-of-pocket costs involved in autism testing.
7. Cost of Autism Screening
7.1 Screening Tools and Instruments
The cost of autism screening can vary depending on the specific tools and instruments used. Some screening tools may be available at no cost, while others may require a fee. The cost of proprietary screening tools or those administered by trained professionals may be higher compared to freely available screening tools or online questionnaires. It is essential to discuss the available screening options and associated costs with healthcare professionals or screening centers.
7.2 Costs of Specific Screening Tests
The costs of specific screening tests can vary depending on factors such as the type of test, the licensing or copyright fees associated with the tool, and the provider or center administering the screening. Some healthcare facilities or clinics may charge a fee for conducting screening tests, while others may offer free or low-cost screenings as part of their services. Researching local options and inquiring about the costs associated with specific screening tests is crucial.
7.3 Importance of Early Screening
Early screening for autism is crucial for timely identification and intervention. Identifying autism early allows individuals and their families to access the necessary resources, services, and support as soon as possible. Early screening can lead to early intervention, which has been shown to improve outcomes for individuals with autism. The potential costs associated with autism screening should not deter individuals from seeking early screening, as the benefits of early identification outweigh the financial considerations.
8. Cost of Comprehensive Autism Assessment
8.1 Components of Comprehensive Assessment
A comprehensive autism assessment typically includes various components, such as detailed developmental history interviews, cognitive assessments, behavioral observations, and evaluations by professionals from different disciplines. The costs of a comprehensive assessment can vary depending on the number and complexity of these components, as well as the professionals involved. It is advisable to discuss the components of the assessment and associated costs with the healthcare provider or diagnostic center.
8.2 Fees for Diagnostic Specialists
Diagnostic specialists, such as psychologists, psychiatrists, or developmental pediatricians, may charge fees for their services as part of the comprehensive autism assessment. The fees for these specialists can vary based on factors such as their experience, expertise, and geographical location. It is important to inquire about the fees charged by diagnostic specialists and discuss any available financial assistance options or payment arrangements.
8.3 Duration of Assessment
The duration of a comprehensive autism assessment can vary depending on factors such as the complexity of the case and the number of professionals involved. Longer assessment sessions or multiple assessment appointments may incur higher costs. Patients should be prepared for the potential costs associated with the duration of the assessment and plan accordingly.
8.4 Follow-up Recommendations
Following a comprehensive assessment, professionals involved may provide recommendations for further evaluations, interventions, or therapies. The costs associated with these follow-up recommendations should be considered when budgeting for autism testing and ongoing support. It is important to consult with healthcare professionals and inquire about the potential costs of recommended services to ensure access to appropriate care.
9. Additional Costs for Genetic Testing
9.1 Types of Genetic Tests
Genetic testing may be recommended as part of the autism diagnostic process to identify specific gene mutations or chromosomal abnormalities associated with autism spectrum disorder. The types of genetic tests recommended depend on the individual’s specific situation and family history. The costs of genetic tests can vary based on the specific type of test, laboratory fees, and associated costs for genetic counseling.
9.2 Charges for Genetic Testing
The charges for genetic testing can vary depending on factors such as the type of test, the laboratory used, and insurance coverage. Some genetic tests may be covered by insurance plans, while others may require out-of-pocket expenses. It is advisable to inquire about the charges for genetic testing, check with the insurance provider for coverage, and discuss potential financial assistance options with healthcare professionals.
9.3 Counseling Expenses
Genetic counseling is often recommended alongside genetic testing to help individuals and families understand the implications of test results, make informed decisions, and receive appropriate support. Genetic counseling expenses can add to the overall costs of genetic testing for autism and should be considered when budgeting for testing. Inquiring about the costs and availability of genetic counseling services is essential for individuals considering genetic testing.
9.4 Benefits of Genetic Testing
While there may be costs associated with genetic testing, it can provide valuable information about the individual’s diagnosis and potentially inform treatment options. Genetic testing can offer individuals and families a better understanding of the underlying genetic factors associated with autism and potentially guide the development of personalized intervention plans. It is important to weigh the benefits of genetic testing against the associated costs and make informed decisions in consultation with healthcare professionals.
10. Financial Aid and Support Programs
10.1 Medical Assistance Programs
Medical assistance programs, such as Medicaid or other state-funded programs, may provide financial aid or coverage for individuals with autism. These programs are often income-based and offer various forms of support, including coverage for diagnostic procedures, assessments, therapies, and medications. It is advisable to research and inquire about the eligibility criteria, application procedures, and covered services under medical assistance programs to determine potential financial aid options.
10.2 Autism-Specific Grants and Scholarships
Several organizations and foundations offer grants or scholarships specifically aimed at supporting individuals with autism and their families. These grants or scholarships may cover the costs of autism testing, evaluation, and other related services. It is recommended to explore such grants and scholarships through autism-specific organizations, local community resources, or online databases to identify potential funding opportunities for autism testing.
10.3 Non-Profit Organizations and Charities
Non-profit organizations and charities focused on autism advocacy and support may offer financial aid or assistance programs. These programs may provide grants, subsidies, or reimbursement for autism testing or related services. Connecting with local or national autism organizations and exploring their support programs is a valuable step in identifying potential financial aid options.
10.4 State and Local Government Support
State and local governments may provide support programs or resources for individuals with autism and their families. These programs may include subsidies, grants, or funding streams specifically aimed at assisting with the costs of autism testing or associated services. It is advisable to contact relevant government agencies or departments, such as departments of health or social services, to inquire about available support programs and financial aid options.
10.5 Fundraising and Community Support
Individuals and families seeking financial aid for autism testing can explore fundraising options and community support. Crowdfunding platforms, local fundraising events, or collaborations with community groups or organizations can help raise funds to offset the costs of autism testing. Engaging with local communities, support groups, or social networks can offer valuable guidance, resources, or financial assistance opportunities.
In conclusion, the costs involved in autism testing can vary depending on several factors, including the type and range of assessments, insurance coverage, additional services required, and geographical location. While costs can be a significant consideration, it is important not to compromise timely and accurate diagnosis. Exploring insurance coverage, financial aid programs, and community resources can help alleviate the financial burden associated with autism testing and ensure individuals with autism receive the necessary evaluations and support they need for their optimal development and well-being.